Vitamin K2 is an important nutrient for optimum health and performance. Unfortunately, many people are not aware of this.
Here is a simple infographic from Chris Masterjohn, PhD detailing why we need vitamin K2 and how we can get it from our diet.
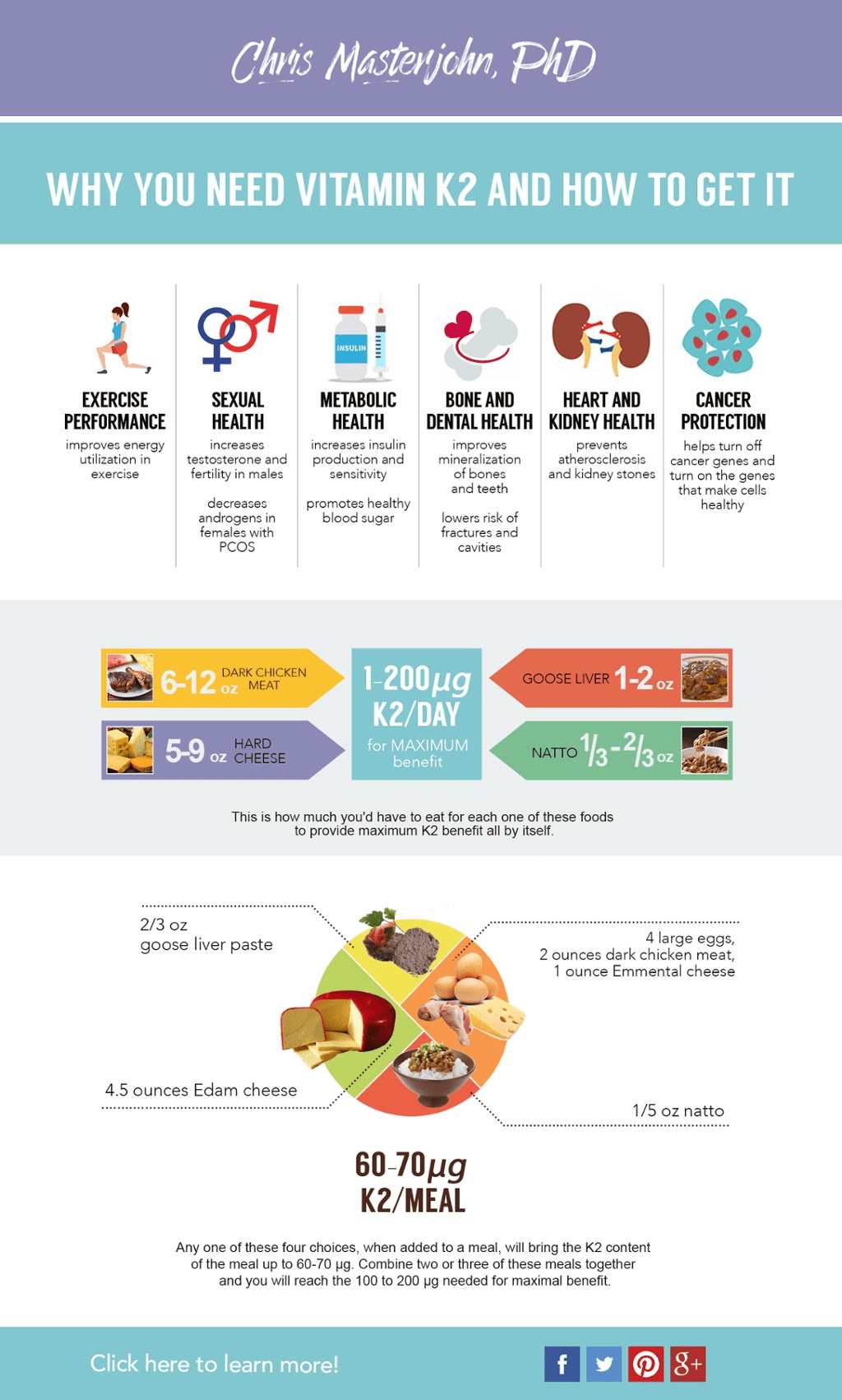
Vitamin K2 is an important nutrient for optimum health and performance. Unfortunately, many people are not aware of this.
Here is a simple infographic from Chris Masterjohn, PhD detailing why we need vitamin K2 and how we can get it from our diet.

Trying to find that right movement that will radically change your body.
Find that missing ingredient to your training programming that will help you build muscle faster, drop fat quicker, along with dominate on any field of play. For most of us it’s as simple as this.
The loaded carry.
Strength coach Dan John states that the loaded carry does more to expand athletic qualities than anything else out there. Because of their versatility, loaded carries can be used by anyone, anywhere. It doesn’t matter if your goal in to get stronger, build muscle, improve overall posture or even lose some body fat.
Loaded carries are very functional. Loaded carries basically work every muscle in the body. Shoulders and upper back, arms, core, and even your legs. By doing them you can improve your strength, stability, and conditioning all at once.
Some variations
Single-handed carries

Two-handed carries
Sandbags, sleds, packs and vests

How often
Do some kind of loaded carry three times a week. Farmers walks and sled push / pulls are my personal favorite moves and tend to be some of the best bang-for-the-buck choices.
Final thoughts
I’ve used many of the variations listed above with success. I’ve found that they have contributed to building muscle, improve posture and body composition and have also helped with overall physical conditioning. As a result, loaded carries regularly find their way into my programming.
A month is all it takes. Try it and get back to me. Three times a week for a month. Obviously, your grip will be better. Your legs will be stronger. You’ll discover that the weight room isn’t that tough any more. You’ll look leaner, but be bigger.
A real game changer.
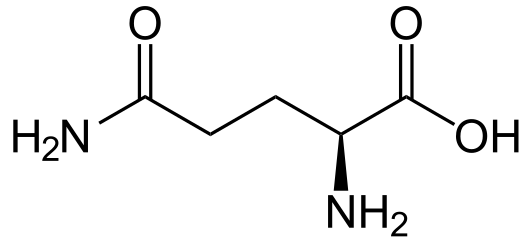
What is it?
L-glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the body, making up approximately 60% of free-form amino acids. Glutamine is highly in demand throughout the body. It is used in the gut and immune system extensively to maintain optimal performance.
When the body is under stress from heavy training, the level of glutamine in the muscles and blood decreases dramatically (up to 50%) as the body produces more white blood cells to fight infection and repair damaged muscle tissue. If the body’s stores of glutamine and capacity to produce it are inadequate to meet the demand, the risk of over-training, illness and injury increases.
Who needs it?
Glutamine has been studied since the 1960’s in the treatment of those suffering from trauma (such as burn, surgery, and disease victims).
To a lesser extent, research has been done on its benefits for athletes. Since athletes use a lot of their glutamine during intense training sessions and competitive events, they are more susceptible to illness, as the immune system relies heavily on this amino acid.
Becoming ill or losing lean muscle mass are signs of a deficiency.
Benefits of taking L-glutamine
Here are some of the ways that glutamine supplementation can boost performance and assist in overall health:

How much should be supplemented?
The dosage relative to the volume of intensity and duration hasn’t been well established, but it appears that supplementing with 5-10 grams on the days of very hard workouts and competitive events may be beneficial. The is no known downside from taking in L-glutamine at these levels, and any excess will be excreted in the urine.
When to supplement?
Take L-glutamine in the evening before bed or in the morning upon waking, when your muscles have been without significant nutrition for up to 8 hours. Research shows that L-glutamine can raise growth hormone levels significantly by taking 5-10 grams before bed.
Another good time for L-glutamine is within an hour post workout. This helps in the recovery process from demanding workouts.
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re looking at increasing your athletic performance, build muscle or improve a health condition such as leaky gut or diabetes, L-glutamine should be a part of your daily diet.
Eat fresh wholefoods that we were evolved to eat. Usually three times a day but occasionally skip a meal, let hunger dictate your meals. Workout with short and intense resistance sessions a few times a week. Walk, play and stay active.
– Arthur De Vany, Ph.D.

Arthur De Vany believes that we have virtually the same genetic makeup as our Paleolithic ancestors who lived 40,000 years ago. The problem, he and many others believe, is that our environment has changed dramatically.
De Vany contends that we would be healthier, fitter, and live longer if we adopted a modern version of the Paleolithic lifestyle. Having spent more than 30 years studying and practicing how to do that, he is regarded by many as the “grandfather” of the Paleo movement.
In this post I am going to sum up some of his basic principles and show you how to get started working out and eating how we evolved to for optimal health.
Nutritional Philosophy
To call a [low-carb] diet on which humans lived for millennia a fad is just ignorant. In fact, it is the modern fad of eating a high carb, high grain, high sugar diet that is harmful.
Arthur De Vany, Ph.D.
Cook by colour and texture so that meals look beautiful. If busy, skip meals with little worry. You don’t have to have three square meals a day. Snack on nuts or celery. Drink plenty of water. Also drink tea, coffee and a little wine.
Basically, eat animal proteins, vegetables, fruits, nuts and seeds. Full fat diary is fine if tolerated.

What is apple cider vinegar?
People have used apple cider vinegar (ACV) for thousands of years. Everyone from the ancient Babylonians to the Greeks used it as a cure-all for all kinds of health ailments.
Like coconut oil and grass-fed butter, ACV is enjoying a comeback among people who care about their health.
Vinegars are a product of fermentation. This is a process in which sugars in a food are broken down by bacteria and yeast. In the first stage of fermentation, the sugars are turned into alcohol. Then, if the alcohol ferments further, you get vinegar. ACV comes from pulverized apples.
ACV contains is acetic acid, which helps get rid of harmful bacteria and fungi in the gastrointestinal tract. This helps the digestion and absorption of nutrients from food in the intestines.
10 reasons to use apple cider vinegar
Hot tip
Heartburn and digestive issues are two of the most common health complaints today. They are some of the standard symptoms that result from the modern westernised diet, which can result in not enough stomach acids being produced by the body (ie: hydrochloric acid).
By adding raw ACV to your diet, you can help your stomach create enough acid to start the digestion process and kill off harmful microbes.
Giving your digestion a boost is easy. Just add ACV to your salad dressings or drink some raw, unfiltered ACV diluted with water about 20 minutes prior to meals.
Cauliflower, like broccoli is a member of the cruciferous family, contains an impressive array of nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and other phytochemicals.
Antioxidants are nature’s way of providing your cells with an adequate defense against attack by excessive amounts of reactive oxygen species. Without an adequate supply of antioxidants to help suppress excess free radicals you raise your risk of oxidative stress, which leads to accelerated tissue and organ damage.
Why it’s a superfood?
Healthy evidence
Numerous studies have linked sulforaphane to reduced cancer rates in humans. A study in the Journal of Nutrition reported that treating liver cells with compounds contained in cauliflower reduced the production of lipids that increase heart disease risk when present in high levels in the blood. Other studies have reported that high intake of cauliflower was associated with a lower risk of an aggressive form of prostate cancer.
Here are some of the science backed health benefits of cauliflower:
Making the most of Cauliflower
The best way to eat cauliflower is raw in fresh salads, as this will retain the vitamin C and other water-soluble nutrients. Cauliflower can be used as a great substitute for potatoes in low carbohydrate nutrition plans.
Steaming cauliflower better preserves the anti-cancer compounds rather than boiling. Better again is a healthy saute. This is done by bring either some bone broth (beef or chicken) or water to boil in a pan then lightly saute the cauliflower florets for approximately five minutes.
Skinny Fat: A physique, while not overweight (and possibly underweight), lacks any visible lean, striated tissue.
– Definition, Urban Dictionary
Conventional wisdom would suggest that if you are overweight you are generally unhealthy, and if you are thin, you are healthy. However, new research points to just how dangerous being skinny can be. Well, if you are a “skinny fat” person, that is.
The medical term for this is metabolically obese normal weight (MONW), or skinny fat. Basically, this means that you are carrying too much body fat and not enough lean muscle (generally belly fat).
Women are more commonly to be hit with MONW syndrome or skinny fat than men. A common theory is that men usually aren’t afraid to lift weight in the gym (and, to be fair, men naturally have more lean muscle than women).
On the other hand, women generally have the misconception that lifting weights immediately makes you look big and bulky (which couldn’t any further from the truth) and prefer group fitness classes like as Zumba and/or Aerobics or spend all of their time on the treadmill, stairmaster or a spin bike, not to mention inventing a million bizarre weight loss diets (with equally bizarre names).
Simply dieting can eliminate weight, but it will not strengthen anything. Also, because of physiology unique to women, the fat cells in the lower body just happen to be world-class hoarders.
Starting at an early age
In America, studies on teenagers found that 37% of skinny children had one or more signs of pre-diabetes, such as high blood pressure, high blood sugar, or high cholesterol. Yes. You read correctly. Almost 4 out of 10 normal-weight children are pre-diabetic!
Nearly one-third of children are overweight or obese in the America. However, it appears that only 20% are healthy. This means that 8 out of 10 children in America are either overweight or have pre-diabetes or type-2 diabetes. Countries like Australia aren’t that far behind.
Processed and fast foods, video games, social media sources, reduced sleep quality and inactivity are all causative factors in developing these conditions in children.
It probably isn’t helping that many of the role models in our society aren’t exactly the picture of health, ie: skinny runway models, or super skinny guys without an ounce of masculinity in them. Whatever happened to the track and field champions of past Olympic Games? Fast, fit, strong, conditioned men and women able to compete in multiple events.

Health issues related to Skinny Fat Syndrome
A person who is skinny fat is susceptible to the following conditions (but not limited to):
How does a person become Skinny Fat?
In no particular order, these are several of the most common ways a person can become skinny fat:
How to turn it all around
Reversing the effects of skinny fat syndrome is very similar to that of someone who is overweight and pre-diabetic. Using the following steps one can easily turn it all around start improving their quality of life:
What is most alarming is that many people who think they get a pass because they are thin should actually be taking a second look at their health. It is possible to be skinny and sick and be metabolically obese, which is potentially even more dangerous.
The good news is that it is a solvable condition. By following the above points or speaking with your medical practitioner you will be well on the way to becoming a healthier person that is full of energy and has a much better overall body composition.
What is a kettlebell?
It’s a cannonball with a handle. It’s an extreme handheld gym. It’s a great strength and conditioning tool.
The kettlebell can deliver high level all-around fitness. Functional strength. Staying power. Flexibility and mobility. Fat loss without the dishonor of an aerobics class. Kettlebells can be used virtually anywhere.
Kettlebells are traditionally measured in poods. An old Russian unit of measure, a single pood weighs 16 kilograms (kg).
The general rule of thumb is that men should start with a 16 kg kettlebell. An experienced athlete can start with a 24 kg kettlebell.
For women, it is suggested that they start with an 8 kg kettlebell and 12 kg if they’re an experienced athlete.
Kettlebell safety 101
Below is a short list of rules on how to use a kettlebell safely as stated in the book Enter the Kettlebell written by kettlebell master trainer Pavel Tsatsouline.
The kettlebell sumo deadlift
The first movement to master is the kettlebell sumo deadlift. This movement requires the athlete to safely pick up the kettlebell from the floor.
Taking a comfortable stance, with feet slightly turned out. Sit back as you would in a high chair, and pick up the kettlebell with both hands by extending your hips and knees.

The checklist:
Once you have mastered this simple and functional movement you will be ready to progress on to more advance kettlebell movements such as:
I have personally used kettlebells with great success over the years and can attribute a large part of my own physical conditioning to the kettlebell.
The burpee is a staple in many conditioning routines, and for good reason. This simple exercise can be done almost anywhere, by almost anyone.
To perform a Burpee:
Burpee benefits
Some of the benefits of adding burpees to your workout routine:
It’s not a Squat Thrust
At first glance, you may associate the burpee with a traditional squat thrust. Squat Thrusts are typically performed without the vertical jump. With a squat thrust, you simply “stand up” before returning to the squat position. Squat thrusts are much easier than explosive burpees.
Variations
There are many variations to performing burpees. Some will lower the intensity, while others will increase it. They include:
With or without weighted resistance (dumbbells, vests, medicine balls, etc.), a regular dose of burpee conditioning will provide immediate, and drastic improvements in your physical fitness.
Burpee Intervals
Burpee Intervals are one of the best conditioning drills. Here is one of my favorite Burpee conditioning workouts from Infinite Intensity by Ross Enamait.
Begin with 30 seconds of Burpees, and immediately follow with 30 seconds of shadow boxing. Continue this pattern for a full 2 or 3-minute round.
The Round
Beginners
Intermediate
Advanced
Master

The first thing to remember is that ANY muscle contraction or physical effort is due to a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). When an ATP molecule is combined with water the last of three phosphate groups splits apart and produces energy. This breakdown of ATP for muscle contraction results in adenosine diphosphate (ADP). The limited stores of ATP must be replenished for the physical effort to continue; so chemical reactions take place to add a phosphate group back to ADP to make ATP.
How ATP is produced
Take three different activities and put them on a continuum. On one end would be a quick, explosive burst such as throwing a punch. On the other end would be an extended, lower-level event such as walking five miles. Between the two could be anything. An intense twenty-second activity, one minute of constant force exertion, or a five-minute event with varied intensities of effort.
The three energy systems
Conventionally, there are three energy systems that produce ATP:
All systems are available and “turn on” at the onset of any activity. What dictates which one (or two) is relied upon the most is the effort required.
ATP-PC system – maximum power / short duration
ATP and phosphocreatine (PC) compose the ATP-PC system, also sometimes called the Phosphogen system. It is immediate and functions without oxygen. It allows for up to approximately 12 seconds (+ or -) of maximum effort. During the first few seconds of any activity, stored ATP supplies the energy. For a few more seconds beyond that, PC cushions the decline of ATP until there is a shift to another energy system.
Examples:

Lactic acid system – moderate power / moderate duration
Now it becomes more complicated as the energy demands shift to this system. The glycolytic or lactic acid system is the “next in line” tool after the ATP-PC system runs its course. Dietary carbohydrates supply glucose that circulates in the blood or is stored as glycogen in the muscles and the liver. Blood glucose and/or stored glycogen is broken down to create ATP through the process of glycolysis. Like the ATP-PC system, oxygen is not required for the actual process of glycolysis (but it does play a role with the by-product of glycolysis: pyruvic acid).
Here is where it gets interesting. After maximum power declines around 12 seconds, further intense activity up to approximately 30 seconds results in lactic acid accumulation, a decrease in power, and consequent muscle fatigue. This high, extended effort is labeled “fast” glycolysis. Exerting further effort up to approximately 60 seconds results in another drop in power due to the shift in dependence on the oxidative system.
Enter “slow” glycolysis into the discussion. Remember that the by-product of glycolysis is pyruvic acid. In fast glycolysis, more power can be generated, but pyruvic acid is converted to lactic acid and fatigue ensues quickly. Slow glycolysis is different. Relatively less power is generated, but pyruvic acid is converted to acetyl coenzyme A (acA), fed through the oxidative Krebs cycle, more ATP is produced, and fatigue is delayed.
Examples:

Aerobic system – low power / long duration
Your maximal effort was fueled initially by the ATP-PC, but your performance declines. Continued effort results in further decline, either via fast glycolysis (quick decline) or slow glycolysis (slower decline). You’re now entering the complex world of the low power but longer duration aerobic or oxidative system.
Examples:
The effort demand is low, but ATP in this system can be produced three ways:
First, the science. The Krebs cycle is a sequence of chemical reactions that continues to oxidize the glucose that was initiated during glycolysis. Remember the acA? It enters the Krebs cycle, is broken down in to carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and “bang” two more ATP molecules are formed.
The problem is, the hydrogen produced in the Krebs’s cycle and during glycolysis causes the muscle to become too acidic if not tended to. To alleviate this, hydrogen combines with several enzymes and is sent to the electron transport chain. Through more chemical reactions in the electron transport chain, hydrogen combines with oxygen, water is produced, and acidity is prevented. Notice this takes time due to the need of oxygen, which is why the oxidative energy takes a while and intensity of effort declines (i.e., max effort sprints become a slow jog/walk).
The Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain metabolize triglycerides (stored fat) and carbohydrates to produce ATP. The breakdown of triglycerides is called lipolysis. The byproducts of lipolysis are glycerol and free fatty acids. However, before free fatty acids can enter the Krebs cycle they must enter the process of beta oxidation, where a series of chemical reactions downgrades them to acA and hydrogen. The acA now enters the Krebs cycle and fat is metabolized just like carbohydrates.
Simply put…
Due to the time-line, the aerobic system provides energy much more slowly than the other two systems, but has an almost unlimited supply (in your adipose tissue – yeah, that fatty stuff you can pinch). The aerobic system by itself is used primarily during complete rest and low-intensity activity. It can produce ATP through either fats (fatty acids) or carbohydrates (glucose).
Hopefully that was simple enough to understand. It is important to have a basic understanding of these energy systems when developing a training program for everybody ranging from the weekend warrior to the elite level athlete.